Mica as an Insulator: A Detailed Guide
Mica possesses excellent electrical insulation properties, featuring high dielectric strength and heat resistance up to 1000°C, making it ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications.
Its unique layered structure and chemical stability enable mica to withstand moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring lasting performance in harsh environments.
Electrical Properties
| Thickness (mm) | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mica | 0.01 | 200 |
| Mica | 0.10 | 115 |
| Mica | 1.00 | 61 |
| Wax Paper | 0.10 | 40-60 |
| Air | 0.2 | 5.75 |
| Air | 0.6 | 4.92 |
| Air | 1.0 | 4.36 |
| Air | 10.0 |
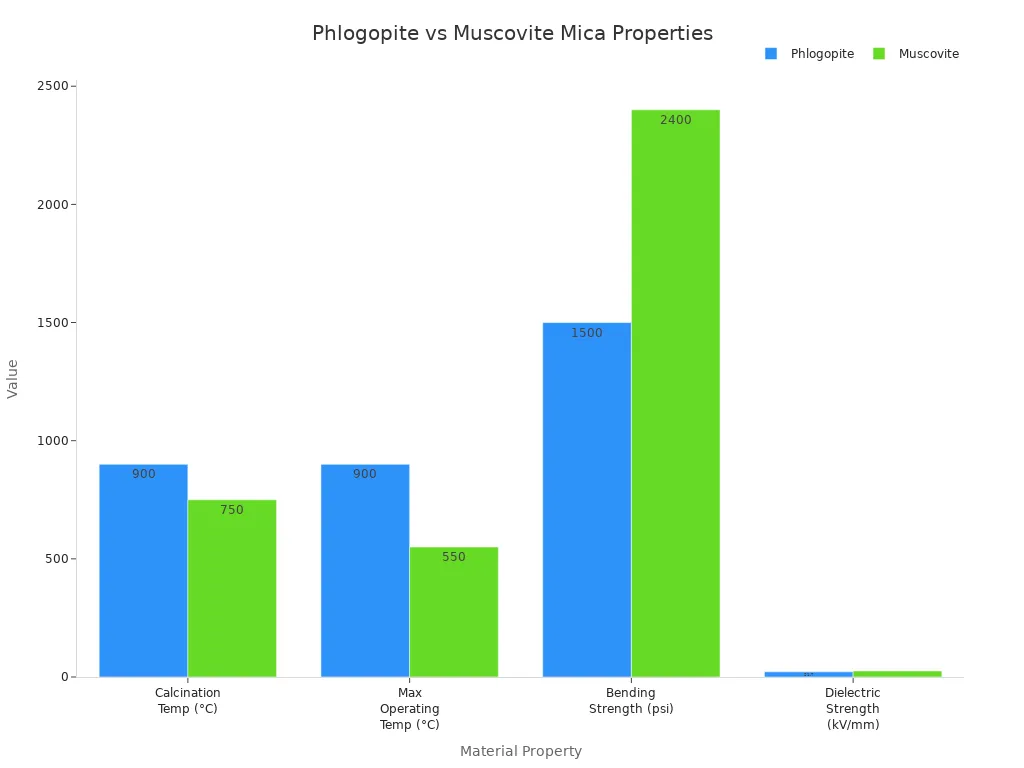
| Mica Type | Maximum Temperature (°C) | Insulation Performance and Application Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Phlogopite | ~1000 | Highest temperature resistance; suitable for industrial high-heat applications; maintains insulation |
| Biotite | 500-700 | Moderate heat resistance; used in construction and automotive components |
| Muscovite | ~500 |
| Mechanical Strength Type | Muscovite (MN/m²) | Phlogopite (MN/m²) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ~175 | ~1000 |
| Shear Strength | 220-270 | 1000-1300 |
| Compressive Strength | 190-285 | N/A |
Layered Structure
Electrostatic forces within the layers add extra stability, helping mica resist electrical breakdown.
When manufacturers exfoliate mica into thinner sheets, its dielectric constant increases. This enhances its insulation capabilities in demanding applications.
The layered design also allows mica to be incorporated into composite materials, where it works alongside other substances to create even stronger insulation.
Mica's structure explains why it works well in everything from circuit boards to industrial furnaces.
Chemical Stability
Muscovite
Muscovite is the most popular mica for electrical insulation. Its light color and transparency make it easy to spot in electronic components. Muscovite is valued for its:
High chemical stability and heat resistance, therefore performing well in harsh environments.
Used for washers, gaskets, and other electrical components where consistent insulation is required.
Muscovite mica can be split into thin, flexible sheets, giving it an advantage in electronics, especially where transparency and reliable insulation are needed.
Phlogopite
Phlogopite mica shines in high-temperature environments. It handles more heat than muscovite, making it ideal for industrial work. Here's a comparison of phlogopite vs. muscovite:
Phlogopite mica works best in fire-resistant cables, furnaces, and steel mills. It maintains its shape and insulating capabilities even when things get hot.
Synthetic mica brings modern advantages to insulation. Manufacturers produce mica with high purity, free from natural impurities. Here's why synthetic mica is increasingly popular:
Better electrical insulation and vacuum degassing, ideal for sensitive electronics.
Free of harmful heavy metals or natural radiation.
Dielectric Strength
High dielectric strength ensures the safety of electrical systems.
Mica prevents energy loss and discharge.
It's suitable for high-voltage equipment such as transformers and capacitors.
Mica's ability to split into thin sheets doesn't reduce its insulating capabilities, making it a favorite in electronics.
Heat Resistance
Mica maintains its shape and strength at extreme temperatures.
It protects sensitive components from overheating.
Mica as an insulator resists chemicals, moisture, and UV rays. It doesn't easily corrode or break down, even in harsh industrial settings. This durability means less maintenance and fewer replacements.
Mica has consistently worked in damp, hot, or corrosive locations.
Mica stands out in several scenarios:
High-voltage insulation, such as generator windings and transformers
Applications requiring flexibility and toughness, unlike brittle ceramics or glass
Fireproof, non-toxic insulation
| Scenarios | Why Choose Mica? |
|---|---|
| High temperature and high voltage | Maintains insulation where plastics fail |
| Flexible insulation needed | Tougher and more adaptable than ceramic/glass |
| Fire-safe and non-toxic | Non-combustible, electrically safe to use |
| Damp or chemical exposure | Maintains insulating capabilities in harsh environments |
Standards
People also want warranties that cover defects. Good support and clear shipping policies also make a difference. Price matters, but quality and technical help often tip the scales.
When picking mica, users match the insulation class to the application. For example:
N-class (up to 200°C+):
Mica sheets can be fragile, so careful handling keeps them in top condition. Workers should:
Lay mica flat in a dry, clean place.
Avoid bending or folding the sheets.
Use gloves to prevent oils from sticking to the surface.
Use sharp tools to cut mica for clean edges.
Test a small sample before full use.
A little care during storage and installation helps mica last longer and perform better.
Mica stands out for its heat resistance, electrical insulation, and durability. The industry trusts its safety and efficiency. Yuefeng Mica provides reliable solutions for demanding jobs.
What makes mica a better insulator than plastic?
Mica can handle higher heat and voltage. Plastics melt or break down under harsh conditions. Mica remains strong and safe in demanding jobs.
Can mica insulators be used outdoors?
Yes, mica resists moisture, UV rays, and chemicals. It performs well in outdoor environments even with rapidly changing weather.
How do you cut or shape mica sheets?
Previous Page








