What Is a Mica Sheet and How Is It Used

Key Takeaways
Mica sheets resist high heat and provide strong electrical insulation, making them ideal for electronics and heating devices.
There are three main types of mica sheets—Muscovite, Phlogopite, and Synthetic—each with unique heat and strength properties for different uses.
You can choose rigid mica sheets for strong, inflexible insulation or flexible sheets for bending and wrapping applications.
Mica sheets are widely used in electronics, heating elements, insulation, and crafts due to their durability, heat resistance, and transparency.
While mica sheets offer many benefits like safety and long life, they can be brittle, costly, and limited in size, so consider these factors when selecting materials.
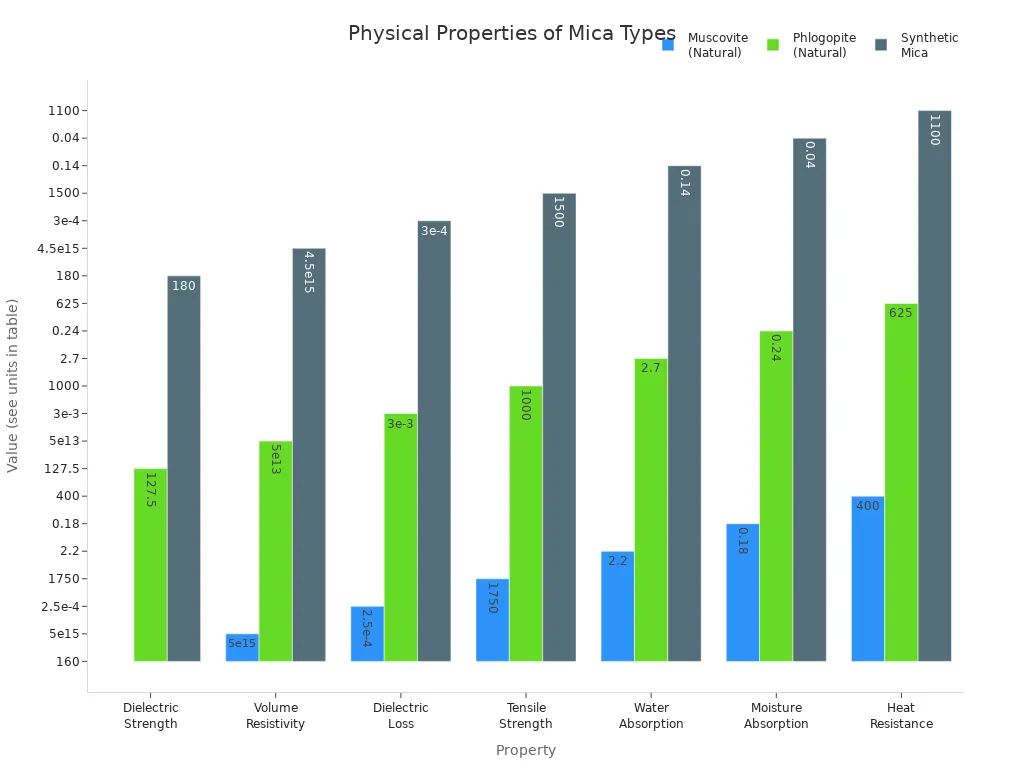
Mica Sheet Properties

Heat Resistance
| Temperature Range (°C) | Temperature Range (°F) | Typical Industrial Applications and Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 500 | Up to 932 | General industrial use; electrical appliances, heating elements, some machinery; moderate heat resistance |
| 500 - 800 | 932 - 1472 | More demanding electrical insulation; electric motors, transformers, heavy-duty electrical equipment; maintains insulation and mechanical strength |
| 800 - 1200 | 1472 - 2192 | Extreme temperature environments; aerospace, advanced electronics, high-temperature furnaces; continuous exposure without significant degradation |
Tip:
Electrical Insulation
You benefit from mica’s high dielectric strength and resistance to corrosion. These properties ensure reliable insulation where other materials may degrade.
Transparency and Durability
Note:
Mica Sheet Types
When you choose a mica sheet, you will find three main types: Muscovite, Phlogopite, and Synthetic. Each type offers unique properties and fits different uses in industry and technology.
Muscovite
Phlogopite
Phlogopite mica appears darker, from yellow to black, and contains more iron and magnesium. You will find that it handles higher temperatures than muscovite, staying stable up to 900°C. This makes phlogopite ideal for high-temperature insulation, especially in environments where heat resistance is critical. It is softer than muscovite, so you may use it in applications where flexibility and softness are needed, such as commutator mica in motors.
Synthetic
Synthetic mica offers:
Higher thermal stability and heat resistance
Better transparency and smoother surfaces
Non-toxic and environmentally friendly properties
Rigid and Flexible Forms
You can select either rigid or flexible mica sheets based on your needs:
Flexible sheets: Producers impregnate mica paper with flexible binders, then roll or press it to the desired thickness. These sheets bend easily and work well as tapes or wraps for cables and heating elements.
Tip: Choose rigid mica sheets for mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Use flexible sheets when you need pliability without losing insulation.
Mica Sheet Uses

Electronics
Mica sheets serve as insulators and heat sinks in devices such as:
Power transistors and heat-generating components
Motors and transformers
Electrical cables (as mica tape)
Tip:
Heating Elements
Here are some ways mica sheets enhance heating elements:
Its durability extends the lifespan of devices, lowering maintenance needs.
Mica’s flexibility allows it to fit complex parts, contributing to reliability.
You will also find mica in space heaters and rice cookers, where it maintains optimal temperatures and ensures even cooking. Mica’s high dielectric strength and thermal stability (up to 1000°C) make it ideal for these demanding environments.
Insulation
Key reasons to choose mica sheets for insulation include:
High durability and mechanical strength for heavy-duty applications.
Chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents.
Versatility—mica sheets can be cut and shaped for specific needs.
Cost-effectiveness due to long-term savings from durability.
Mica’s electrical insulation properties make it suitable for insulating electronic components and industrial equipment. You will see mica sheets used in furnace insulation, automotive gaskets, and as barriers in power cables to prevent electrical arcing.
FAQ
What is the main difference between natural and synthetic mica sheets?
You will find that synthetic mica sheets have higher purity and fewer defects than natural mica. Synthetic mica resists higher temperatures and offers better consistency. Natural mica comes from mining, while synthetic mica is made in a lab.
Can you cut mica sheets at home?
You can cut thin mica sheets with scissors or a utility knife. For thicker sheets, use a fine-toothed saw. Always wear gloves and a mask to protect yourself from dust and sharp edges.
Are mica sheets safe for food contact?
You can use mica sheets in appliances like microwaves and toasters. Manufacturers design food-safe mica sheets to withstand heat and not release harmful substances. Always check product labels for food safety certification.
How do you clean mica sheets?
You can wipe mica sheets with a soft, damp cloth. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive pads. For stubborn stains, use mild soap and water. Dry the sheet completely before reinstalling or using it.
What should you do if a mica sheet cracks?
Previous Page
Next Page








